Gum Disease and Mask Mouth
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a serious oral health condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. It is caused by the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and gums. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and other serious health problems.
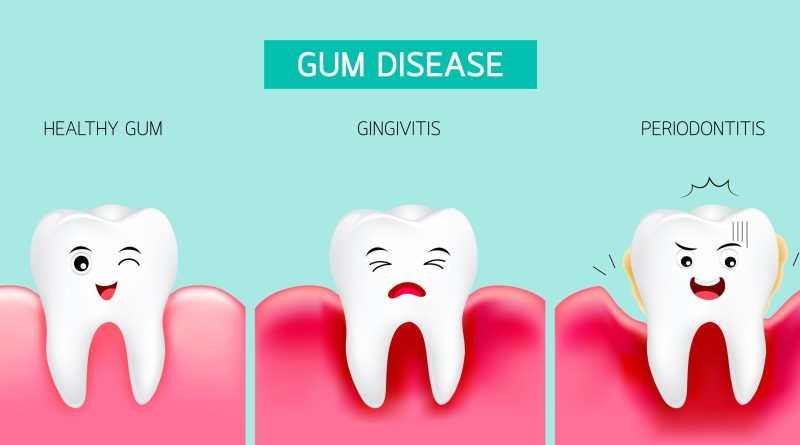
There are two main stages of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease and is characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily when brushed or flossed. At this stage, the condition is reversible with proper oral hygiene and dental treatment.
However, if gingivitis is not treated, it can progress to periodontitis, the more advanced stage of gum disease. Periodontitis is characterized by the loss of bone and connective tissue supporting the teeth, leading to the teeth becoming loose and eventually falling out. It is important to catch and treat gum disease in its early stages to prevent it from progressing to periodontitis.
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing gum disease, including poor oral hygiene, tobacco use, diabetes, hormonal changes, and certain medications. Stress and a diet high in sugar and processed foods can also contribute to the development of gum disease.
One of the main challenges in preventing and treating gum disease is the lack of symptoms in the early stages. Many people may not realize they have gum disease until it has progressed to the more advanced stages, making it important to visit a dental professional regularly for checkups and cleanings.
In addition to regular dental visits, good oral hygiene is crucial in preventing gum disease. This includes brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash to remove plaque and bacteria from the mouth. It is also important to limit sugary and processed foods in the diet, as these can contribute to the buildup of plaque.
Treatment for gum disease depends on the severity of the condition. In the early stages of gingivitis, a professional cleaning and improved oral hygiene may be enough to reverse the condition. More advanced stages of gum disease may require more intensive treatment, such as scaling and root planing, where the dentist removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline, or gum surgery to remove infected tissue and repair damage to the gums and supporting structures of the teeth.
While gum disease is a serious and potentially damaging condition, it is also preventable and treatable with proper oral hygiene and regular dental visits.
Mask mouth, on the other hand, is a relatively new oral health condition that has emerged as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. Mask mouth is characterized by dry mouth, bad breath, and an increase in oral health problems such as tooth decay and gum disease.
Wearing a mask can cause dry mouth by trapping moisture and reducing saliva flow, which is essential for keeping the mouth hydrated and healthy. Saliva helps to neutralize acids produced by bacteria in the mouth, as well as wash away food particles and plaque. Without enough saliva, bacteria can thrive and lead to tooth decay and gum disease.
Mask wearing can also contribute to bad breath by trapping bacteria and odors inside the mask. The combination of dry mouth and trapped bacteria can lead to an increase in bad breath and halitosis.
To prevent mask mouth, it is important to drink plenty of water and use a mouthwash to help keep the mouth hydrated and clean. It is also important to continue practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash. If dry mouth is a problem, using a saliva substitute or chewing gum can help stimulate saliva production.